Hello world
I’m Hassan Adams, a resilient black British videographer, and I come from the challenging backdrop of South London. Born in the UK, I’ve channeled my unwavering passion for videography into my successful video production company. Despite the daily juggling act of university studies, business commitments, and even the occasional Amazon delivery, I’m an outgoing and hard-working young man, ceaselessly pursuing excellence in all facets of my life. My journey embodies determination and the relentless pursuit of greatness.
Understanding the Two-Step Flow Theory: A Paradigm Shift in Communication
Introduction
The Two-Step Flow Theory, proposed by Paul Lazarsfeld and Elihu Katz in the 1950s, challenged the traditional linear communication model. This theory presents a unique perspective on how information and influence are disseminated within society, highlighting the crucial role of opinion leaders in shaping public opinion and behaviour. In this blog post, we will delve into the Two-Step Flow Theory, exploring its key concepts and implications for modern communication and media.
The Traditional Linear Model
Before delving into the Two-Step Flow Theory, it is crucial to understand the traditional linear model of communication. In this model, information flows from mass media sources, such as newspapers and television, directly to the general public. The assumption is that people passively consume this information, and its impact is uniform across all recipients.
Two-Step Flow Theory: A Paradigm Shift
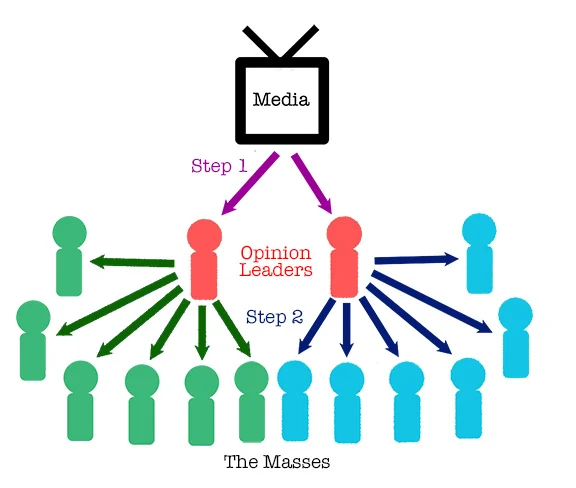
The Two-Step Flow Theory challenges this one-way flow of information by introducing a more complex and interactive process. According to this theory, information from mass media does not directly affect the general public. Instead, it first reaches opinion leaders, individuals who are well-informed and active in a specific field or subject matter. These opinion leaders, in turn, influence those around them, known as the “opinion followers.”
Opinion Leaders
Opinion leaders play a pivotal role in the Two-Step Flow Theory. They are passionate, knowledgeable, and highly engaged in a particular domain, whether politics, fashion, technology, or any other subject. These opinion leaders actively seek information from mass media and other sources, critically evaluate it, and form their own opinions. As they interact with others, they share their views and information, effectively acting as intermediaries between mass media and the general public.
Opinion Followers
Opinion followers, on the other hand, are the people who look up to and trust the opinion leaders. They are less likely to be active information seekers and often rely on opinion leaders to give them insights and perspectives. These followers adopt the views and opinions of their leaders, making the opinion leaders the primary influencers in shaping their beliefs and behaviours.
Implications for Modern Communication
The Two-Step Flow Theory has several implications for modern communication, particularly in the digital age:
- Social Media and Influencer Marketing: Social media platforms have amplified the role of opinion leaders, giving rise to influencers with substantial followings in various niches. These influencers wield significant power in shaping public opinion and consumer behaviour. Marketers have capitalized on this by utilizing influencer marketing strategies to reach their target audiences through trusted intermediaries.
- Filter Bubbles and Echo Chambers: In the digital landscape, people often form online communities that reinforce their existing beliefs and opinions. Opinion leaders within these communities can further entrench these views, creating filter bubbles and echo chambers. Recognizing the existence of such bubbles is essential for media literacy and fostering diverse perspectives.
- Political Polarization: The Two-Step Flow Theory helps explain political polarization, where opinion leaders within different ideological camps influence their followers, resulting in deep divisions and limited exposure to alternative viewpoints.
- News Consumption: Understanding the theory can also show how people consume news. Those who follow opinion leaders with a specific bias may be exposed to a particular narrative. In contrast, those who follow opinion leaders from different backgrounds may have a more balanced perspective.
Conclusion
The Two-Step Flow Theory revolutionized our understanding of communication and the role of opinion leaders in shaping public opinion and behaviour. In today’s interconnected world, where information flows rapidly through various channels, this theory remains relevant. By recognizing the influence of opinion leaders and the dynamics of the two-step flow, we can better navigate the complex landscape of modern communication, media, and information dissemination.
Construction of Identity in a Digital World: Shaping the Self in the Virtual Realm
Introduction
In an increasingly digital world, our identities are no longer confined to the physical realm; they have extended into the vast landscape of the internet. Identity construction in a digital world is a complex and ever-evolving process shaped by our interactions, choices, and the platforms we engage with. This blog post delves into how digital technology has transformed how we perceive and craft our identities, exploring the implications, opportunities, and challenges it presents.
The Digital Persona: A New Frontier
The digital world offers us the opportunity to create and curate multiple personas. These digital personas may align with or diverge from our offline selves, presenting us with new ways to express our identities. Social media profiles, online avatars, and pseudonyms contribute to this rich tapestry of digital identities, offering individuals a canvas to project different aspects of themselves.
- Identity Exploration: In the digital realm, individuals can explore various facets of their identities without the constraints of the physical world. They can experiment with different interests, beliefs, and expressions, allowing personal growth and self-discovery.
- Digital Avatars: Virtual spaces and online gaming have popularized the use of avatars вАУ digital representations of users. These avatars can be customized to reflect an idealized version of oneself or even adopt entirely different personas, offering freedom and creativity in identity expression.
The Perils of Anonymity
While the internet provides a platform for identity exploration, it also harbours the anonymity that can lead to toxicity and deceit. Anonymity allows individuals to behave in ways they might not in the physical world, leading to online harassment, trolling, and even spreading false information.
- Online Harassment: The ability to hide behind a screen name can embolden some to engage in cyberbullying or harassment, causing actual harm to others and making online spaces less safe.
- Disinformation: False identities and pseudonyms make it easier to spread disinformation, contributing to the erosion of trust in online spaces and beyond.
- Impersonation: The ease of creating fake profiles makes it possible for individuals to impersonate others, leading to identity theft and reputational damage.
Digital Identity in the Professional Sphere
The digital world has also transformed how we present ourselves professionally. LinkedIn profiles, personal websites, and professional social networks like Twitter allow individuals to build their brand and share their expertise.
- Personal Branding: Many professionals have cultivated personal brands through consistent online presence and sharing their expertise. This has opened up new opportunities for networking, job hunting, and thought leadership.
- Cybersecurity and Privacy: However, sharing personal information online raises concerns about data security and privacy. It is essential to balance the benefits of professional identity building with safeguarding one’s personal information.
Conclusion
The construction of identity in a digital world is a multi-faceted process with both advantages and challenges. It provides a space for exploration and self-expression, allows for the creation of multiple personas, and facilitates professional identity building. However, it also carries the risks of anonymity, online harassment, and the spread of disinformation.
As we navigate the digital landscape, it is crucial to be mindful of the choices we make when it comes to digital identity. We must strike a balance between authenticity and the personas we create, be responsible digital citizens, and consider the ethical implications of our actions online.
In this dynamic digital age, our identities evolve, shaped by online interactions and the platforms we engage with. Embracing the opportunities and challenges presented by the digital realm, we can construct identities that are meaningful, authentic, and reflective of the multidimensional individuals we are in both the physical and virtual worlds.



Hi Hassan!! Your post was very informative – you mentioned that social media gives users opportunities to express themselves in various different forms, through avatars, profiles and many more. Do you think that now due to the advancement in technology, the digital world has given us more creative freedom than in real physical life? And do you think there are any limitations/risks of this if it continues to give us more creative expression of our online identities?
Also, do you have any social media profile anywhere where we can see your videography? I’d love to connect with more creatives!!