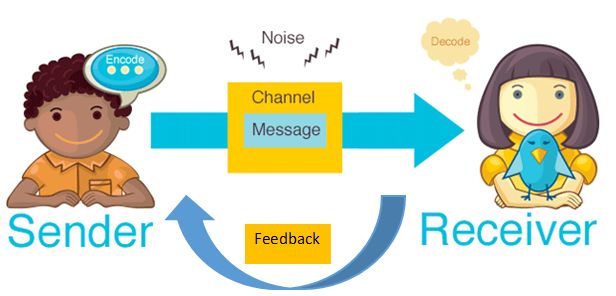
As explained by Stuart Hall, encoding and decoding is a way of understanding the theoretical approach to how messages in media are produced, disseminated, and understood. Hall suggested that as viewers are dependent on their own social surroundings and have the power to modify communications through group activity, they can actively participate in the figuring out of signals. (Lucy Glasspool, 2020)
There are various interpretations about encoding and decoding, but how exactly does this theory apply to the present day? LetвАЩs have a modern discussion about the not-so-ancient hypothesis!
In the era of everything digital, social media has allowed individuals to be themselves by sharing opinions, stories, and experiences. This way of sharing things on social media involves processes of encoding and decoding that shape the narratives.
Every single individual on social media has to create or portray their identities in the world of digital media. Whether it is your profile on Instagram or LinkedIn, you have to create an identity for people to perceive and understand you as an individual. Social interactions through platforms like Instagram, Twitter, Facebook, etc. such as likes, comments, shares, and emojis, are like social signals that people decode to gain popularity, social approval, and engagement. This online behaviour talks about the impact of feedback and the psychological aspects of social comparisons.
Visual encoding refers to the cognitive process by which humans convert visual stimuli, such as images, objects, or scenes, into a mental representation that can be stored and retrieved within the memory system. (Chris Drew, 2023) Visual encoding is one of the most crucial aspect when it comes to users encoding the message. If we talk about Instagram, users carefully select what kind of images they want to post using filters and captions. This is how users encode narratives, which their followers then decode to create engagement in the online community.
While there are not many films that directly address the encoding and decoding model, “The Truman Show,” starring Jim Carrey, had elements and themes related to the theory. To explain the movie in a sentence, the main lead, Truman Burbank, was unknowingly living his entire life as the star of a reality television show. That was how the show’s creator encoded his entire life to create a good narrative, and then how Truman gradually decoded and questioned his reality. This movie talked about media manipulation and the role of the audience.
“Inception”, a 2020 film directed by Christopher Nolan, is a noteworthy example of a film that allows viewers to understand a story in a variety of ways. The Science fiction thriller “Inception” explores the idea of shared dreaming and goes into the world of dreams. While all the people who watched the movie were left awestruck by the story, some were still trying to figure out what the ending was. This kind of narration requires a level of understanding, and Nolan carefully crafted and encoded the message, which the audience figured out by decoding the ending.
Reference list:
Glasspool, Lucy. 2020. Encoding/Decoding. The Japanese media and popular culture. Available at: https://jmpc-utokyo.com/author/glasspool/
Drew, C. (March 29, 2023). Visual Encoding: 10 examples and Definition. Helpful Professor. https://helpfulprofessor.com/visual-encoding/




Hi Srushti!! I really liked your examples of films when discussing the ideas of encoding and decoding – will have to give The Truman Show a watch! Visual encoding is also a new term that I had not heard of before, so it is quite interesting to know that there is actually a term for the transformation of visual stimuli into a mental representation by the audience. Do you think that cultural, societal, or individual differences can influence the encoding and decoding process, particularly in a globally connected digital landscape?
Srushti – I really enjoyed your post as your examples of social media and film have given this theory a relatable context. I had never seen encoding and decoding contextualised in relation to social media, so this really made me think as I had previously thought that only companies had control over this encoding process. Individuals now have the power to shape their own public perception through the way they encode messages about themselves, through word, and content choices on their feeds! I wonder if you feel that individuals encode their feeds based on how they view themselves, or how they think the world will view them?